The science behind the fire triangle explains how fires ignite and sustain themselves. The fire triangle represents the three components needed for a combustion reaction: heat, fuel, and oxygen. When one or more elements of a fire triangle are present, a chemical reaction will occur, producing various flames. The combustion triangle varies depending on the different materials and conditions of the burning material.
For example, the type of fuels, the gas release, and the amount of air can affect how a flame sustains and burns. The concept of the fire triangle or combustion triangle is crucial in fire protection and combustible materials. If you’ve suffered from burn injuries in a fire or explosion accident, a Chicago fire accident lawyer at Curcio & Casciato can help you seek justice.
Fire Triangle Definition
The fire triangle or combustion triangle is a simple model that explains what fires require to start and sustain through a chemical reaction. The fire triangle consists of three elements or three components needed: heat, fuel, and oxygen.
Heat raises the temperature of the combustible material to its ignition point, oxygen from the surrounding air supports the chemical reaction, and the fuel source, such as gas, flammable materials, or a free radical, provides the different materials needed to burn.
For effective fire prevention, removing or controlling one or more elements out of the three elements or three components needed to burn in the fire triangle will disrupt the chemical reaction by removing what the fire needs to sustain.
3 Elements of Fire Triangle
The fire triangle or combustion triangle requires breaking down its three elements: heat, fuel, and oxygen. These components must be present for a fire to start and sustain. Each being an important factor for combustion reactions. Removing one of the components needed would extinguish the fire.
By learning how these different materials and components interact within the combustion triangle, fuels or free radical sources, heat, and air, we can better grasp how fire extinguishers work, how to store flammable materials, and take steps to prevent and control electrical and gas fires effectively.

Heat Source
Within the fire triangle, heat provides the energy to ignite or sustain an exothermic reaction which will lead to combustion. Radiant heat, friction, or electrical energy can produce heat that raises the temperature of a substance to its ignition point.
Once materials reach ignition temperature, an exothermic reaction occurs, releasing energy in the form of heat and resulting in a fire. This continuous release of energy keeps the fire burning, provided the other elements of the fire triangle, fuel and oxygen, are present.
Flash Point vs Fire Point
The flash point is the lowest heat at which a fuel can vaporize to form a mixture that will ignite in the air. However, at the flash point, the fire will not sustain itself.
The fire point is the temperature at which the material produces enough vapor to maintain the combustion reaction after exposure to an ignition source. The fuel source will continue to burn if the temperature remains above the fire point, which explains why some fires extinguish themselves quickly.
Fuel Sources
Fuel sources are the materials that provide the substance for a combustion reaction to occur. Once components required to ignite appear, burning fuel will sustain a fire, and different types of fuel burn at various rates and intensities.
Fires require solid fuel, liquid, free radical, or gaseous fuels, each of which behave differently during the combustion reaction leading the the fire. Burning metals like magnesium or aluminum can pose unique challenges, as they require higher temperatures to ignite and often produce intense, sustained flames.
What is a Flashover?
A flashover occurs when all combustible materials simultaneously reach their ignition temperatures and ignite, leading to a rapid spread of flames and fire.
What is a Backdraft?
A backdraft happens when a fire, deprived of oxygen, smolders but continues to produce combustible gas. When oxygen is suddenly reintroduced, often by opening a door, these unburned gases can ignite explosively with the surrounding air.
Oxygen Supply
Oxygen is the third essential component in the fire triangle. For a fire to sustain, there must be sufficient oxygen to support the combustion reaction. In most cases, normal ambient air contains around 21% oxygen, enough to sustain most fires. If the oxygen concentration drops below a certain level, the fire will be extinguished by oxygen deprivation.
Fire Tetrahedron: The Chemical Chain Reaction
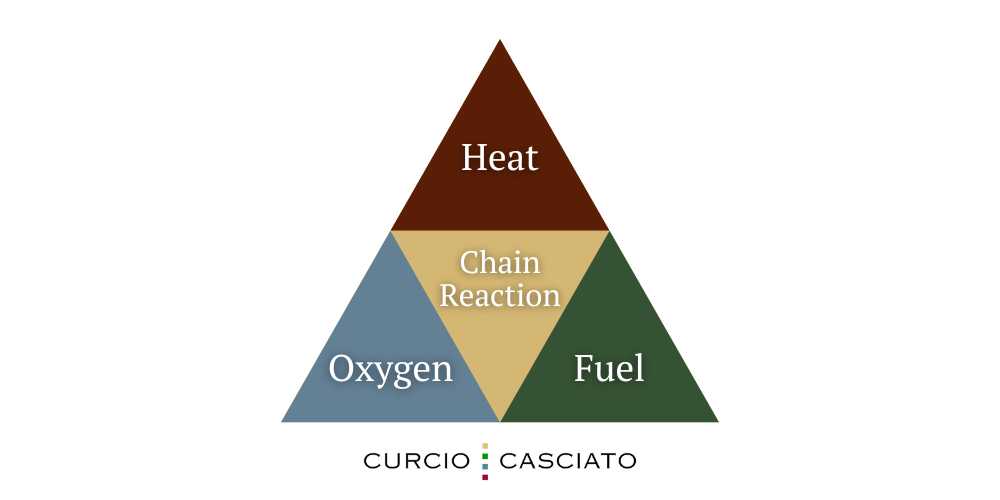
The fire tetrahedron is an expanded model of the fire triangle, adding a fourth element: the chemical chain reaction. While the fire triangle focuses on the three components needed to start a fire, the fourth element in the fire tetrahedron represents the importance of the continuous chain reaction that occurs once a fire has ignited. This chemical chain reaction sustains the process by allowing the interaction between heat, fuel, and oxygen to propagate. Without this chain reaction, the fire could not continue to burn.
Like the fire triangle, disruption in one fire tetrahedron element will cause the fire to be extinguished.
For example, using carbon dioxide to suppress a fire works by both displacing oxygen or air and interrupting the chemical chain reaction. The fire tetrahedron provides a more complete understanding of fire dynamics and is particularly useful in flame suppression strategies.
Why is Understanding the Chemical Reaction Important for Fire Safety
In the fire tetrahedron, the chemical chain reaction is the process that keeps a fire burning by continuously feeding the combustion reactions between heat, fuel, and oxygen. Interrupting this chain reaction within the fire tetrahedron can be the key to extinguishing the flame.
Fire safety tools, such as a fire blanket or fire extinguishers work to disrupt these combustion reactions by cutting off the oxygen or making it difficult to produce heat. For example, fire extinguishers work by displacing oxygen or inhibiting the chemical chain reaction, while fire blankets smother the fire, cutting off its oxygen supply.
Why Must Fire Extinguishers Be Routinely Maintained?
Fire extinguishers are crucial tools in fire protection, providing a first line of defense against the fire tetrahedron. Over time, fire extinguishers can lose pressure, have damaged components, or even become obstructed, making them unreliable against fires.
Regular maintenance checks ensure that they can disrupt the fire tetrahedron by eliminating the oxygen around the flames.

How the Fire Triangle Affects Personal Injury Lawsuits
The fire triangle plays a significant role in personal injury lawsuits involving fire accidents. In many cases, liability may depend on whether one or more of these three components were improperly managed or allowed to exist in hazardous conditions.
For example, a property owner might be held accountable if faulty electrical wiring provided the heat source, or if flammable materials were left near ignition sources, causing a fire to start. Additionally, inadequate fire protection systems that fail to disrupt the fire triangle can lead to greater injuries and damages, increasing the potential for lawsuits.
Fire vs Explosion
While both fires and explosions are dangerous, they differ in their causes and effects. Fires typically start the fire triangle components come together, resulting in slow or gradual burns.
Explosions involve a sudden release of energy, often from rapid combustions or pressure buildup, leading to a violent blast. The key distinction lies in the speed of the reaction: fires develop slowly, while explosions occur instantaneously.

Who is Liable for Fire Damage in Illinois?
Liability for fire damage in Illinois depends on the circumstances of the fire’s origin. Property owners, landlords, manufacturers, and even utility companies may be held responsible if their negligence contributed to the fire.
A Chicago burn injury lawyer can help fire accident victims evaluate the situation, determine fault for the fire, and pursue financial compensation.
Can You Sue Neighbor for Fire Damage in Illinois?
In Illinois, you can sue a neighbor for fire damage if their negligence or intentional actions caused the fire. For example, if a neighbor failed to maintain their property or started an uncontrolled fire, damaging your property, they could be held liable for burn injuries and property damage caused by the fire.
Can I Sue My Landlord for Electrical Fire in Illinois?
If an electrical fire occurs due to unsafe conditions or a landlord’s failure to maintain the property, you may be able to file a lawsuit. A Chicago premises liability attorney can help tenants prove that the landlord’s negligence, such as failing to fix faulty wiring or not installing proper fire alarms, contributed to the fire.
Can I Sue My Employer for an Explosion Accident in Illinois?
If you were injured in an explosion at work, you may have grounds to sue your employer. In some cases, workers’ compensation may not cover all damages, and a lawsuit may be necessary to pursue further compensation. A Chicago work injury lawyer can assist in determining the cause of the explosion or fire and help pursue fair financial compensation.
My Car Caught on Fire, Can I Sue in Illinois?
If your car caught fire due to a defect or malfunction, you may be able to pursue legal action against the manufacturer or other responsible parties. Chicago product liability lawyers can help investigate whether a defective part, design flaw, or improper manufacturing caused the fire.
Can You Sue a Fire Department for Negligence in Illinois?
Suing a fire department for negligence in Illinois can be challenging due to legal protections for government entities. However, if the fire department’s actions or inaction directly contributed to the damage or injuries, it may be possible to sue the government in Illinois. These cases require proving gross negligence or failure to perform essential duties, such as improperly fighting a fire or causing delays in response.

How a Chicago Explosion Accident Lawyer Can Help
If you or a loved one has been involved in a fire or explosion accident in Chicago, it’s important to seek legal help as soon as possible. With a deep understanding of how the fire triangle affects fire and explosion accident liability, our fire accident lawyers will investigate your case and hold the responsible parties accountable. Contact us today for a free consultation and let a personal injury lawyer in Chicago help protect your rights.



